 tel
tel
tel
tel
 tel
tel
tel
tel

2023-03-30 11:17:30
Introduction to the basic principles of infrared
Light is an electromagnetic wave, and the visible light that our human eyes see only accounts for a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. In nature, there are also a large number of non visible electromagnetic waves, which like visible light and constitute the radiation intensity distribution of scenery. The wavelength range of visible light is 380 nm to 780 nm, and the wavelengths are divided into red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue, and violet light from long to short. The wavelength longer than red light is called infrared light, with a wavelength between 1 mm and 760 nm. The spectrum is located outside the red light. Any object in nature that has a temperature higher than absolute zero (- 273.15 ° C) will generate electromagnetic waves with information about the temperature characteristics of the object's surface. Different materials, different temperatures, different surface luminosity, different colors, etc., emit different infrared radiation intensities
Basic Introduction and Application of Short Wave Infrared
The spectral segment with a high transmittance when sunlight penetrates the atmosphere is commonly referred to as the atmospheric window. From 1um to 14um, there are three "atmospheric windows" defined as: short wave (SWIR): 1um – 3um, medium wave (MWIR): 3um – 5um, and long wave (LWIR): 8um – 14um.
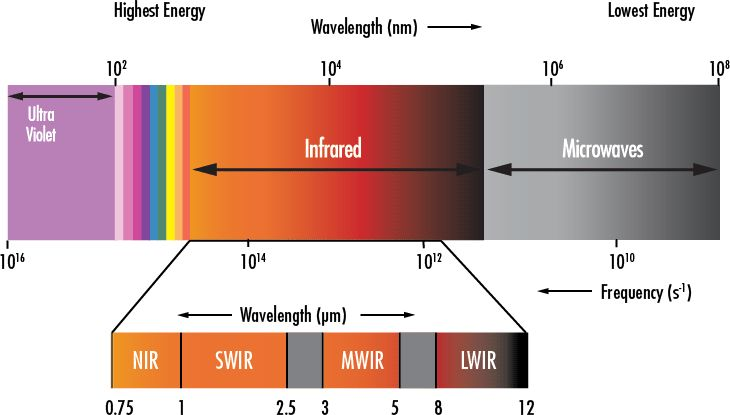
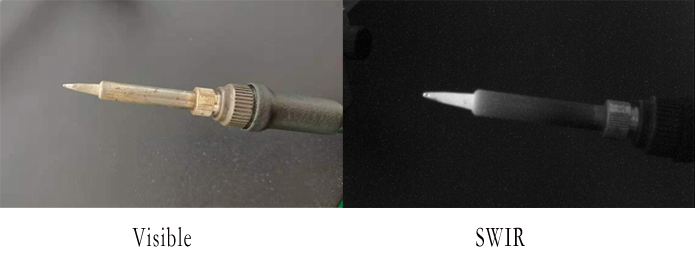
The short wave infrared band refers to the band with a wavelength between 1000-3000 nm, which cannot be recognized by the naked eye. Minerals, artificial substances, and other ground objects have special components that can be "seen" by short-wave infrared light, but cannot be seen by the naked eye and visible light in near-infrared light.
Although thermal imaging can detect warm objects in cold backgrounds, short wave infrared cameras can recognize what the object is because thermal imagers cannot provide the resolution and dynamic range that can be achieved using InGaAs short wave infrared focal plane arrays.
So why use short-wave infrared? Because short-wave infrared has the following advantages:
★ High sensitivity
★ High resolution
★ Able to observe under the glow of the night sky
★ Day and night imaging
★ Can see hidden lasers and beacons
★ No need for low-temperature cooling
★ Conventional low-cost visible light lenses can be used
★ Small size, low power
Shortwave infrared applications
① Low light imaging
② Medical and scientific imaging
③ Hyperspectral imaging
④ Laser spot tracking imaging
⑤ High temperature thermal imaging
⑥ Search and rescue remote sensing
⑦ Camouflage recognition
⑧ Waste sorting
⑨ Semiconductor inspection



Sales Manager: Lily Liu
Mobile: 086-13359283296
Email: info@gatherstarhk.com
Gatherstar Technology (HK) Ltd is specialized in infrared and laser photoelectric system products and module, components and elements. we are not only confident in supplying qualified optoelectronic products to all of our customers, but also concentrating on offering continuous innovations and reliable service.
